References
1. Mandel P, Metais P. Les acides nucleiques du plasma sanguin chez l’Homme. C R Acad Sci Paris 1948;142:241-3.
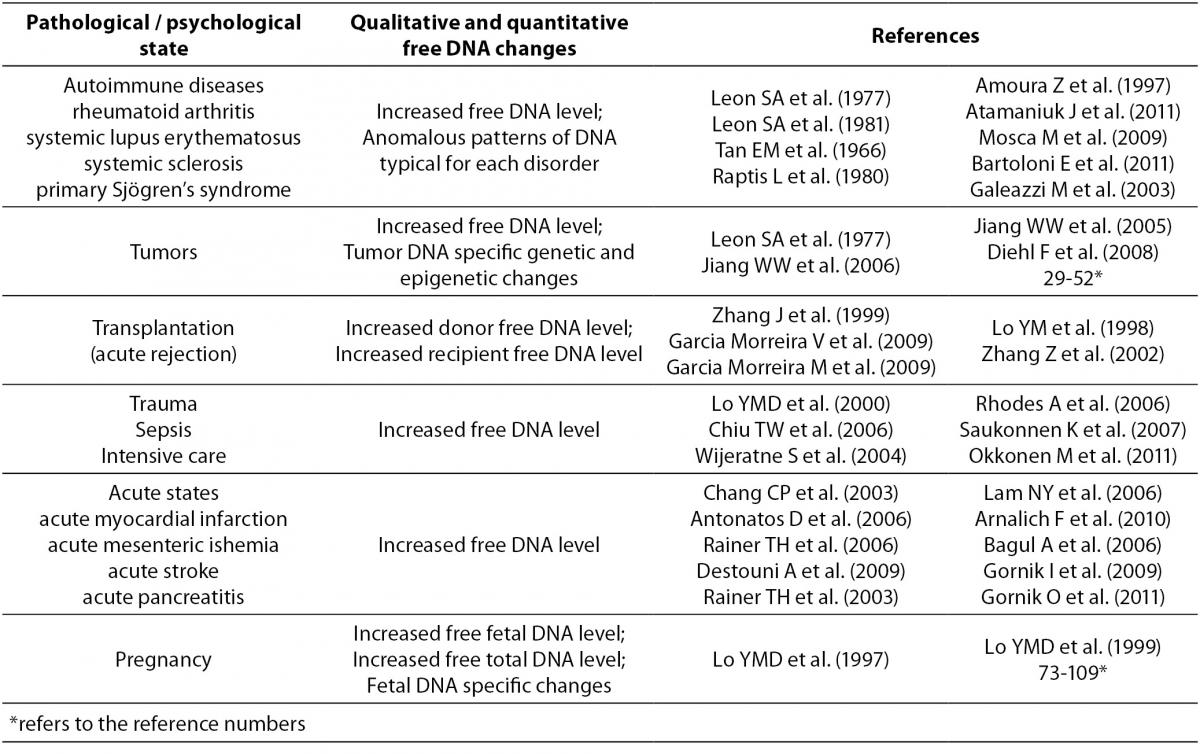
2. Leon SA, Shapiro B, Sklaroff DM, Yaros MJ. Free DNA in the Serum of Cancer Patients and the Effect of Therapy. Cancer Res 1977;37:646-50.
3. Lo YMD, Corbetta N, Chamberlain PF, Rai V, Sargent IL, Redman CWG, Wainscoat JS. Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet 1997;350:485–7.
4. Zhang J, Tong KL, Li PKT, Chan AYW, Yeung CK, Pang CCP, et al. Presence of Donor- and Recipient-derived DNA in Cell-free Urine Samples of Renal Transplantation Recipients: Urinary DNA Chimerism. Clin Chem 1999;45:1741-6.
5. Garcia Moreira V, Prieto Garcia B, Baltar Martin JM, Ortega Suarez F, Alvarez FV. Cell-Free DNA as a Noninvasive Acute Rejection Marker in Renal Transplantation. Clin Chem 2009;55:1958-66.
6. Su YH, Wang M, Brenner DE, Ng A, Melkonyan H, Umansky S, et al. Human Urine Contains Small, 150 to 250 Nucleotide-Sized, Soluble DNA Derived from the Circulation and May Be Useful in the Detection of Colorectal Cancer. J Mol Diagn 2004;6:101-7.
7. Botezatu I, Serdyuk O, Potapova G, Shelepov V, Alechina R, Molyaka Y, et al. Genetic Analysis of DNA Excreted in Urine: A New Approach for Detecting Specific Genomic DNA Sequences from Cells Dying in an Organism. Clin Chem 2000;46:1078-84.
8. Jiang WW, Rosenbaum E, Mambo E, Zahurak M, Masayesva B, Lopes Carvalho A, et al. Decreased Mitochondrial DNA Content in Posttreatment Salivary Rinses from Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:1564-9.
9. Jiang WW, Masayesva B, Zahurak M, Carvalho AL, Rosenbaum E, Mambo E, et al. Increased Mitochondrial DNA Content in Saliva Associated with Head and Neck Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:2486-91.
10. Diehl F, Schmidt K, Durkee KH, Moore KJ, Goodman SN, Shuber AP, et al. Analysis of Mutations in DNA Isolated From Plasma and Stool of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Gastroenterology 2008;135:489-98.
11. Leon SA, Revach M, Ehrlich GE, Adler R, Petersen V, Shapiro B. DNA in synovial fluid and the circulation of patients with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1981;24:1142-50.
12. Rhodes CH, Honsinger C, Sorenson GD. Detection of tumor-derived DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1994;53:364-8.
13. Hickey KP, Boyle KP, Jepps HM, Andrew AC, Buxton EJ, Burns PA. Molecular detection of tumour DNA in serum and peritoneal fluid from ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer 1999;80:1803–8.
14. Anker P, Stroun M. Circulating DNA in plasma or serum. Medicina (B Aires) 2000;60:699-702.
15. Jahr S, Hentze H, Englisch S, Hardt D, Fackelmayer FO, Hesch RD, Knippers R. DNA Fragments in the Blood Plasma of Cancer Patients: Quantitations and Evidence for Their Origin from Apoptotic and Necrotic Cells. Cancer Res 2001;61:1659-65.
16. Fournié GJ, Courtin JP, Laval F, Chalé JJ, Pourrat JP, Pujazon MC, et al. Plasma DNA as a marker of cancerous cell death. Investigations in patients suffering from lung cancer and in nude mice bearing human tumours. Cancer Lett 1995;91:221-7.
17. Stroun M, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Olson-Sand A, Anker P. About the possible origin and mechanism of circulating DNA: Apoptosis and active DNA release. Clin Chim Acta 2001;313:139-42.
18. van der Vaart M, Pretorius PJ. The Origin of Circulating Free DNA. Clin Chem 2007;53:2215.
19. Tsumita T, Iwanaga M. Fate of injected deoxyribonucleic acid in mice. Nature 1963;198:1088-9.
20. Lo YMD, Zhang J, Leung TN, Lau TK, Chang AMZ, Hjelm NM. Rapid Clearance of Fetal DNA from Maternal Plasma. Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:218-24.
21. Tan EM, Schur PH, Carr RI, Kunkel HG. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Antibodies to DNA in the Serum of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1966;45:1732-40.
22. Raptis L, Menard HA. Quantitation and Characterization of Plasma DNA in Normals and Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1980;66:1391-9.
23. Amoura Z, Piette JC, Chabre H, Cacoub P, Papo T, Wechsler B. Circulating plasma levels of nucleosomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: correlation with serum antinucleosome antibody titers and absence of clear association with disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40: 2217-25.
24. Atamaniuk J, Hsiak YY, Mustak M, Bernhar, Erlacher L, Fodinger M. Analysing cell-free plasma DNA and SLE disease activity. Eur J Clin Invest 2011;41:579-83.
25. Barteloni E, Ludovini V, Alunno A, Pistola L, Bistoni O, Crino L, et al. Increased levels of circulating DNA in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: A possible marker of disease activity in Sjogren’s syndrome. Lupus 2011;20:928-35.
26. Mosca M, Giuliano T, Cuomo G, Doveri M, Tani C, Curcio M, et al. Cell-free DNA in the plasma of patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 2009;28:1437-40.
27. Galeazzi M, Morozzi G, Piccini M, Chen J, Bellisai F, Fineschi S, Marcolongo R. Dosage and characterization of circulating DNA: present usage and possible applications in systemic autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun Rev 2003;2:50-5.
28. Salamunic I. Laboratory diagnosis of autoimmune diseases – new technologies, old dilemmas. Biochem Med 2010;20:45–56.
29. Stroun M, Anker P, Maurice P, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Beljanski M. Neoplastic characteristics of the DNA found in the plasma of cancer patients. Oncology 1989;46:318-22.
30. Sorenson GD, Pribish DM, Valone FH, Memoli VA, Bzik DJ, Yao SL. Soluble Normal and Mutated DNA Sequences from Single-Copy Genes in Human Blood. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1994;3:67-71.
31. Vasioukhin V, Anker P, Maurice P, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Stroun M. Point mutations of the N-ras gene in the blood plasma DNA of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1994;86:774-9.
32. Castells A, Puig P, Mora J, Boadas J, Boix L, Urgell E, et al. K-ras Mutations in DNA Extracted From the Plasma of Patients With Pancreatic Carcinoma: Diagnostic Utility and Prognostic Significance. J Clin Oncol 1999;17:578-84.
33. Mulcahy H, Farthing MJ. Diagnosis of pancreatico-biliary malignancy: detection of gene mutations in plasma and stool. Ann Oncol 1999;10:114-7.
34. Hibi K, Robinson CR, Booker S, Wu L, Hamilton SR, Sidransky D, et al. Molecular Detection of Genetic Alterations in the Serum of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancer Res 1998;58:1405-7.
35. Diehl F, Li M, Dressman D, He Y, Shen D, Szabo S, et al. Detection and quantification of mutations in the plasma of patients with colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:16368-73.
36. Zitt M, Müller HM, Rochel M, Schwendinger V, Zitt M, Goebel G, et al. Circulating cell-free DNA in plasma of locally advanced rectal cancer patients undergoing preoperative chemoradiation: a potential diagnostic tool for therapy monitoring. Dis Markers 2008;25:159-65.
37. Kopreski MS, Benko FA, Kwee C, Leitzel KE, Eskander E, Lipton A, Gocke CD. Detection of mutant K-ras DNA in plasma or serum of patients with colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 1997;76:1293-9.
38. Wong IHN, Lo YMD, Zhang J, Liew CT, Ng MHL, Wong N, et al. Detection of Aberrant p16 Methylation in the Plasma and Serum of Liver Cancer Patients. Cancer Res 1999;59:71-3.
39. Chan KC, Lai PB, Mok TS, Chan HL, Ding C, Yeung SW, Lo YM. Quantitative analysis of circulating methylated DNA as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chem 2008;54:1528-36.
40. Yoon KA, Park S, Lee SH, Kim JH, Lee JS. Comparison of circulating plasma DNA levels between lung cancer patients and healthy controls. J Mol Diagn 2009;11:182-5.
41. Chen XQ, Stroun M, Magnenat JL, Nicod LP, Kurt AM, Lyautey J, et al. Microsatellite alterations in plasma DNA of small cell lung cancer patients. Nat Med 1996;2:1033-5.
42. Nawroz H, Koch W, Anker P, Stroun M, Sidransky D. Microsatellite alterations in serum DNA of head and neck cancer patients. Nat Med 1996;2:1035-7.
43. Capone RB, Pai SI, Koch WM, Gillison ML, Danish HN, Westra WH, et al. Detection and Quantitation of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in the Sera of Patients with HPV-associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:4171-5.
44. Mutirangura A, Pornthanakasem W, Theamboonlers A, Sriuranpong V, Lertsanguansinchi P, Yenrudi S, et al. Epstein-Barr Viral DNA in Serum of Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:665-9.
45. Silva JM, Dominguez G, Garcia JM, Gonzalez R, Villanueva MJ, Navarro F, et al. Presence of Tumor DNA in Plasma of Breast Cancer Patients: Clinicopathological Correlations. Cancer Res 1999;59:3251-6.
46. Kohler C, Radpour R, Barekati Z, Asadollahi R, Bitzer J, Wight E, et al. Levels of plasma circulating cell free nuclear and mitochondrial DNA as potential biomarkers for breast tumors. Mol Cancer 2009;8:105.
47. Chun FKH, Muller I, Lange I, Friedrich MG, Erbersdobler A, Karakiewicz PI, et al. Circulating tumour-associated plasma DNA represents an independent and informative predictor of prostate cancer. BJU Int 2006;98:544-8.
48. Mehra N, Penning M, Maas J, van Daal N, Giles RH, Voest EE. Circulating Mitochondrial Nucleic Acids Have Prognostic Value for Survival in Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:421-6.
49. Ellinger J, Albers P, Müller SC, von Ruecker A, Bastian PJ. Circulating mitochondrial DNA in the serum of patients with testicular germ cell cancer as a novel noninvasive diagnostic biomarker. BJU Int 2009;104:48-52.
50. Rogers A, Joe Y, Manshouri T, Dey A, Jilani I, Giles F, et al. Relative increase in leukemia-specific DNA in peripheral blood plasma from patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. Blood 2004;103:2799-801.
51. Deligezer U, Yaman F, Erten N, Dalay N. Frequent copresence of methylated DNA and fragmented nucleosomal DNA in plasma of lymphoma patients. Clin Chim Acta 2003;335:89-94.
52. Hohaus S, Giachelia M, Massini G, Mansueto G, Vannata B, Bozzoli V, et al. Cell-free circulating DNA in Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann Oncol 2009;20:1408-13.
53. Lo YM, Tein MS, Pang CC, Yeung CK, Tong KL, Hjelm NM. Presence of donor-specific DNA in plasma of kidney and liver-transplant recipients. Lancet 1998;351:1329-30.
54. Zhang Z, Ohkohchi N, Sakurada M, Mizuno Y, Miyagi S, Satomi S, et al. Analysis of urinary donor-derived DNA in renal transplant recipients with acute rejection. Clin Transplant 2002;16:45-50.
55. García Moreira V, García BP, Martínez TC, Álvarez Menéndez FV. Elevated transrenal DNA (cell-free urine DNA) in patients with urinary tract infection compared to healthy controls. Clin Biochem 2009;42:729-31.
56. Lo YMD, Rainer TH, Chan LYS, Hjelm NM, Cocks RA. Plasma DNA as a Prognostic Marker in Trauma Patients. Clin Chem 2000;46:319-23.
57. Chiu TW, Young R, Chan LY, Burd A, Lo DY. Plasma cell-free DNA as an indicator of severity of injury in burn patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 2006;44:13-7.
58. Wijeratne S, Butt A, Burns S, Sherwood K, Boyd O, Swaminathan R. Cell- free plasma DNA as a prognostic marker in intensive treatment unit patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004;1022:232-8.
59. Rhodes A, Wort SJ, Thomas H, Collinson P, Bennett ED. Plasma DNA concentration as a predictor of mortality and sepsis in critically ill patients. Crit Care 2006;10:R60.
60. Saukkonen K, Lakkisto P, Varpula M, Varpula T, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Pettilä V, Pulkki K. Association of cell-free plasma DNA with hospital mortality and organ dysfunction in intensive care unit patients. Intensive Care Med 2007;33:1624-7.
61. Saukkonen K, Lakkisto P, Pettila V, Varpula M, Karlsson S, Ruokonen E, Pulkki K. Cell-Free Plasma DNA as a Predictor of Outcome in Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Clin Chem 2008;54:1000-7.
62. Okkonen M, Lakkisto P, Karhonen AA, Parviai-nen I, Reinikainen M, Varpula T, et al. Plasma cell-free DNA in patients needing mechanical ventilation. Crit Care 2011;15:R196.
63. Chang CP, Chia RH, Wu TL, Tsao KC, Sun CF, Wu JT. Elevated cell-free serum DNA detected in patients with myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta 2003;327:95-101.
64. Antonatos D, Patsilinakos S, Spanodimos S, Korkonikitas P, Tsigas D. Cell-Free DNA Levels as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Ann NY Acad Sci 2006;1075:278-81.
65. Rainer TH, Lam NY, Man CY, Chiu RW, Woo KS, Lo YM. Plasma beta-globin DNA as a prognostic marker in chest pain patients. Clin Chim Acta 2006;368:110-3.
66. Destouni A, Vrettou C, Antonatos D, Chouliaras G, Traeger-Synodinos J, Patsilinakos S, et al. Cell-free DNA levels in acute myocardial infarction patients during hospitalization. Acta Cardiol 2009;64:51-7.
67. Rainer TH, Wong LKS, Lam W, Yuen E, Lam NYL, Metreweli C, Lo YMD. Prognostic Use of Circulating Plasma Nucleic Acid Concentrations in Patients with Acute Stroke. Clin Chem 2003;49:562-9.
68. Lam NY, Rainer TH, Wong LK, Lam W, Lo YM. Plasma DNA as a prognostic marker for stroke patients with negative neuroimaging within the first 24 h of symptom onset. Resuscitation 2006;68:71-8.
70. Bagul A, Pushpakom S, Boylan J, Newman W, Siriwardena AK. Quantitative Analysis of Plasma DNA in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. JOP 2006;7:602-7.
71. Gornik I, Wagner J, Gasparovic V, Lauc G, Gornik O. Free serum DNA is an early predictor of severity in acute pancreatitis. Clin Biochem 2009;42:38-43.
72. Gornik O, Gornik I, Wagner J, Radic D, Lauc G. Evaluation of cell free DNA in plasma and serum as early predictors of severity in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2011;40:787-8.
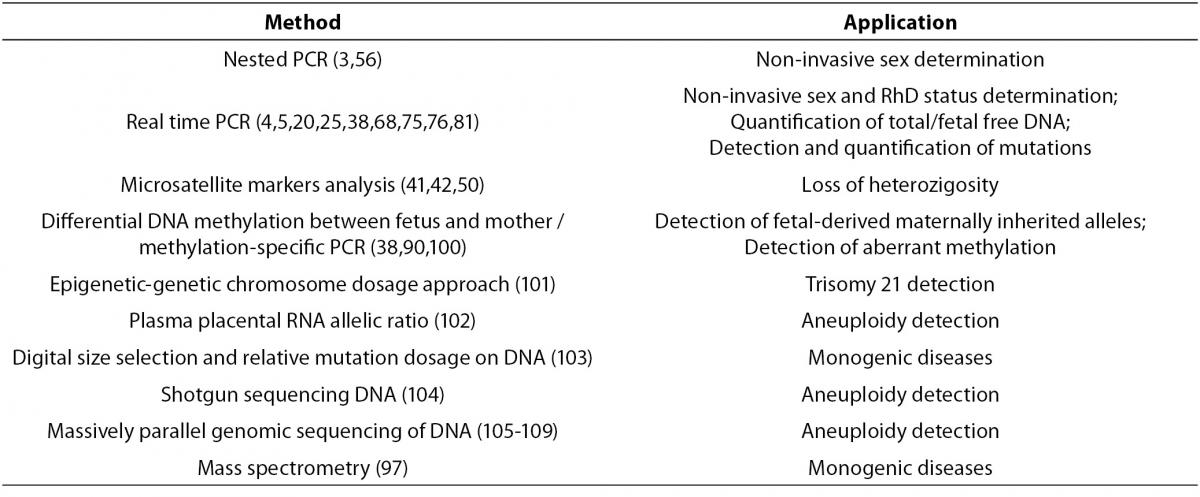
73. Honda H, Miharu N, Ohashi Y, Samura O, Kinutani M, Hara T, Ohama K. Fetal gender determination in early pregnancy through qualitative and quantitative analysis of fetal DNA in maternal serum. Hum Genet 2002;110:75-9.
74. Lun FMF, Chiu RWK, Chan KCA, Leung TY, Lau TK, Lo YMD. Microfluidics Digital PCR Reveals a Higher than Expected Fraction of Fetal DNA in Maternal Plasma. Clin Chem 2008;54:1664-72.
76. Rijnders JPR, van der Schoot CE, Bossers B, de Vroede MAMJ, Christiaens GCML. Fetal Sex Determination From Maternal Plasma in Pregnancies at Risk for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:374-8.
77. Finning KM, Chitty LS. Non-invasive fetal sex determination: Impact on clinical practice. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;13:69-75.
78. Lo YMD, Hjelm NM, Fidler C, Sargent IL, Murphy MF, Chamberlain PF, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal RhD status by molecular analysis of maternal plasma. N Engl J Med 1998;339:1734-8.
79. Finning KM, Martin PG, Soothill PW, Avent ND. Prediction of fetal D status from maternal plasma: introduction of a new noninvasive fetal RHD genotyping service. Transfusion 2002;42:1079-85.
80. Finning K, Martin P, Summers J, Massey E, Poole G, Daniels G. Effect of high throughput RHD typing of fetal DNA in maternal plasma on use of anti-RhD immunoglobulin in RhD negative pregnant women: prospective feasibility study. BMJ 2008;336:816-8.
81. Leung TN, Zhang J, Lau TK, Hjelm NM, Lo YMD. Maternal plasma fetal DNA as a marker for preterm labour. Lancet 1998;352:1904-5.
83. Zhong XY, Holzgreve W, Li JC, Aydinli K, Hahn S. High levels of fetal erythroblasts and fetal extracellular DNA in the peripheral blood of a pregnant woman with idiopathic polyhydramnios: case report. Prenat Diagn 2000;20:838-41.
85. Zhong XY, Holzgreve W, Hahn S. The levels of circulatory cell free fetal DNA in maternal plasma are elevated prior to the onset of preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 2002;21:77-83.
86. Lau TK, Lo KW, Chan LY, Leung TY, Lo YM. Cell-free fetal deoxyribonucleic acid in maternal circulation as a marker of fetal-maternal hemorrhage in patients undergoing external cephalic version near term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:712-6.
87. Sekizawa A, Jimbo M, Saito H, Iwasaki M, Sugito Y, Yukimoto Y, et al. Increased Cell-free Fetal DNA in Plasma of Two Women with Invasive Placenta. Clin Chem 2002;48:353-4.
88. Chan KCA, Ding C, Gerovassili A, Yeung SW, Chiu RWK, Leung TN, et al. Hypermethylated RASSF1A: A Universal Fetal DNA Marker. Clin Chem 2006;52:2211-8.
89. Chiu RWK, Lau TK, Leung TN, Chow KCK, Chui DHK, Lo YMD. Prenatal exclusion of thalassaemia major by examination of maternal plasma. Lancet 2002;360:998-1000.
90. Amicucci P, Gennarelli M, Novelli G, Dallapiccola B. Prenatal Diagnosis of Myotonic Dystrophy Using Fetal DNA Obtained from Maternal Plasma. Clin Chem 2000;46:301-2.
91. Saito H, Sekizawa A, Morimoto T, Suzuki M, Yanaihara T. Prenatal DNA diagnosis of a single gene disorder from maternal plasma. Lancet 2000;356:1170.
95. Majer S, Bauer M, Magnet E, Strele A, Giegerl E, Eder M, et al. Maternal urine for prenatal diagnosis-an analysis of cell-free fetal DNA in maternal urine and plasma in the third trimester. Prenat Diagn 2007;27:1219–23.
96. Shekhtman EM, Anne K, Melkonyan HS, Robbins DJ, Warsof SL, Umansky SR. Optimization of Transrenal DNA Analysis: Detection of Fetal DNA in Maternal Urine. Clin Chem 2009;55:723-9.
97. Sharma VK, Vouros P, Glick J. Mass spectrometric based analysis, characterization and applications of circulating cell free DNA isolated from human body fluids. Int J Mass Spectrom 2011;304:172-83.
98. Dhallan R, Au WC, Mattagajasingh S, Emche S, Bayliss P, Damewood M, et al. Methods to increase the percentage of free fetal DNA recovered from the maternal circulation. JAMA 2004;291:1114-9.
99. Poon LLM, Leung TN, Lau TK, Chow KCK, Lo YMD. Differential DNA Methylation between Fetus and Mother as a Strategy for Detecting Fetal DNA in Maternal Plasma. Clin Chem 2002;48:35-41.
100. Tong YK, Jin S, Chiu RWK, Ding C, Allen Chan KC, Leung TY, et al. Noninvasive Prenatal Detection of Trisomy 21 by an Epigenetic–Genetic Chromosome-Dosage Approach. Clin Chem 2010; 56:190-8.
101. Lo YM, Tsui NB, Chiu RW, Lau TK, Leung TN, Heung MM, et al. Plasma placental RNA allelic ratio permits noninvasive prenatal chromosomal aneuploidy detection. Nat Med 2007;13:218-23.
102. Lun FMF, Tsui NBY, Chan KCA, Leung TY, Lau TK, Charoenkwand P, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic diseases by digital size selection and relative mutation dosage on DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:19920-5.
103. Fan HC, Blumenfeld YJ, Chitkara U, Hudgins L, Quake SR. Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:16266-71.
104. Chiu RWK, Chan KCA, Gao Y, Lau VYM, Zheng W, Leung TY, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:20458-63.
105. Sehnert AJ, Rhees B, Comstock D, de Feo E, Heilek G, Burke J, Rava RP. Optimal Detection of Fetal Chromosomal Abnormalities by Massively Parallel DNA Sequencing of Cell-Free Fetal DNA from Maternal Blood. Clin Chem 2011;57:1042-9.
106. Ehrich M, Deciu C, Zwiefelhofer T, Tynan JA, Cagasan L, Tim R, et al. Noninvasive detection of fetal trisomy 21 by sequencing of DNA in maternal blood: a study in a clinical setting. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:1-11.
107. Palomaki GE, Kloza EM, Lambert-Messerlian GM, Haddow JE, Neveux LM, Ehrich M, et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to detect Down syndrome: An international clinical validation study. Genet Med 2011;13:913-20.
108. Chiu RWK, Akolekar R, Zheng YWL, Leung TY, Sun H, Allen Chan KC, et al. Non-invasive prenatal assessment of trisomy 21 by multiplexed maternal plasma DNA sequencing: large scale validity study. BMJ 2011;342:c7401.
109. Chen EZ, Chiu RWK, Sun H, Akolekar R, Allen Chan KC, Leung TY, et al. Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Trisomy 18 and Trisomy 13 by Maternal Plasma DNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011;6:e21791. 110. Fournié GJ, Martres F, Pourrat JP, Alary C, Rumeau M. Plasma DNA as cell death marker in elderly patients. Gerontology 1993;39:215-21.
111. Zachariah R, Schmid S, Radpour R, Buerki N, Fan AX, Hahn S, et al. Circulating cell-free DNA as a potential biomarker for minimal and mild endometriosis. Reprod Biomed Online 2009;18:407-11.
112. Scalzo PL, Ikuta N, Cardoso F, Regner A, Teixeira AL. Quantitative plasma DNA analysis in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 2009;452:5-7
113. Swarup V, Srivastava AK, Padma MV, Rajeswari MR. Quantifi cation of Circulating Plasma DNA in Friedreich’s Ataxia and Spinocerebellar Ataxia Types 2 and 12. DNA Cell Biol 2011;30:389-94.
114. Ye L, Ma GH, Chen L, Li M, Liu JL, Yang K, et al. Quantifi cation of circulating cell-free DNA in the serum of patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Lung 2010;188:469-74.
115. Atamaniuk J, Vidotto C, Kinzlbauer M, Bachl N, Tiran B, Tschan H. Cell-free plasma DNA and purine nucleotide degradation markers following weightlifting exercise. Eur J Appl Physiology 2010;110:695-701.
116. Wichmann D, Panning M, Quack T, Kramme S, Burchard GD, Grevelding C, Drosten C. Diagnosing Schistosomiasis by Detection of Cell-Free Parasite DNA in Human Plasma, PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2009;3:e422.
117. Barrett AN, Zimmermann BG, Wang D, Holloway A, Chitty LS. Implementing Prenatal Diagnosis Based on Cell-Free Fetal DNA: Accurate Identifi cation of Factors Aff ecting Fetal DNA Yield. PLoS ONE 2011;6 e25202.
118. Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoff el S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, et al. Primer-directed enzymatic amplifi cation of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988;239:487-91.
119. Guidi GC, Salvagno GL. Reference intervals as a tool for total quality management. Biochem Med 2010;20:165-72.
120. Lo YMD, Allen Chan KC, Sun H, Chen EZ, Jiang P, Lun FMF. Maternal Plasma DNA Sequencing Reveals the GenomeWide Genetic and Mutational Profi le of the Fetus. Prenatal Diagn 2010;2:61-9