Impact of the phlebotomy training based on CLSI/NCCLS H03-A6 – procedures for the collection of diagnostic blood
Gabriel Lima-Oliveira
[*]
[1]
Giuseppe Lippi
[2]
Gian Luca Salvagno
[3]
Martina Montagnana
[3]
Geraldo Picheth
[4]
Gian Cesare Guidi
[5]
[1] Laboratory of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Life and Reproduction Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, Italy, Post-Graduate Program of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Department of Medical Pathology Federal University of Parana, Curitiba, Parana, Brazil, MERCOSUL: Sector Committee of Clinical Analyses and in Vitro Diagnostics – CSM 20, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Brazilian Society of Clinical Analyses on Sao Paulo State, Brazil
[2] U.O. Diagnostica Ematochimica, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma, Parma, Italy
[3] Laboratory of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Life and Reproduction Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
[4] Post-Graduate Program of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Department of Medical Pathology Federal University of Parana, Curitiba, Parana, Brazil
[5] Laboratory of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Life and Reproduction Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, Italy, Post-Graduate Program of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Department of Medical Pathology Federal University of Parana, Curitiba, Parana, Brazil
Introduction
The interest in quality improvement and patient safety has been the focus of several national and international initiatives, which have globally led to substantial improvements (1-6). The vast majority of errors in laboratory diagnostics are concentrated in the extra-analytical phase (2,7-13). The preanalytical phase is described as the dark side of the moon in diagnostic process. Errors in pre-analytical phase generate further work or additional investigation that may cause unnecessary procedures for patients and cost to the health care systems (14,15). Preanalytical issues have downstream impact on the use of laboratory resources, hospital costs and overall quality of care. The clinical laboratory results are an essential part of the healthcare delivery. It has been estimated that 60 up to 70% of medical decisions and procedures, such as drug prescriptions, assessments prior to and in the course of further investigations or dialysis, are strongly dependent upon laboratory data (16). Nowadays many procedures are performed and/or oriented by non-laboratory professionals (e.g. nurses, non-technician personnel and administrative staff). A superficial knowledge of the importance of details such as a) adequate fasting time before blood collection (17); b) tourniquet application time (18-24) c) use of appropriate tubes (25-27) and additives (28); d) a series of factors or conditions closely associated with the specimen collection, such as inadequate fulfilling to the rigorous criteria of correct blood drawing, use of tubes containing different additive and/or anti coagulants, incomplete filling, inadequate mixing of the tubes or hemolysis (29-35) are able by themselves either singularly or collectively to strongly influence many laboratory results and thereby affect the diagnostic outcome, the follow-up or even the treatment of the patients.Since 1977, the Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) has recognized the need to put significant attention toward the pre-examination components of laboratory testing, including the correct collection and handling of blood specimens (36). In 2009 Simundic et al. (37) applied a cross-sectional multicentric survey study in some developing European countries and Mexico, aimed at assess the quality of the extra-analytical phase of laboratory activities. This survey showed that the phlebotomy is the most critical activity in the extra-analytical phase (37). The procedures involving phlebotomy, critical for obtaining diagnostic blood specimens, are poorly studied as regards the major sources of errors and the procedures related to quality control process (19). The aim of this study was to verify the compliance with CLSI documents of clinical laboratories from South America and to assess whether teaching phlebotomists to follow the exact procedure for blood collection by venipuncture from CLSI/NCCLS H03-A6 - Procedures for the Collection of Diagnostic Blood Specimens by Venipuncture (36) might improve the quality of the process.
Materials and methods
Data collected
A survey was sent in September 2011 by mail to 3674 laboratories from South America to verify the use of CLSI documents. The questions were:
i) Do you use standardized operating procedures in all your laboratory activities?
ii) If yes, what steps of your laboratory process are based on CLSI guidelines?
( ) pre-analytical
( ) analytical
( ) post-analytical
( ) my processes are not based in CLSI guidelines
iiia) If you marked “my processes are not based in CLSI guidelines”, then specify where your procedures are based.
iiib) If you have checked the above preanalytical option, do you currently employ the CLSI H03-A6 document (36) to standardize your procedures for blood collection by venipuncture?
iv) If yes, do your phlebotomists perform the blood collection by venipuncture following the exact venipuncture procedure from page 5 item 8 of CLSI H03-A6 document (36)?
vi) If not, what did you change in this procedure? And why did you change this procedure?
All the evaluated laboratories signed a formal consent to participate in this study, all laboratory identification was sealed and the project was approved by our Internal Review Board.
Phlebotomy training program
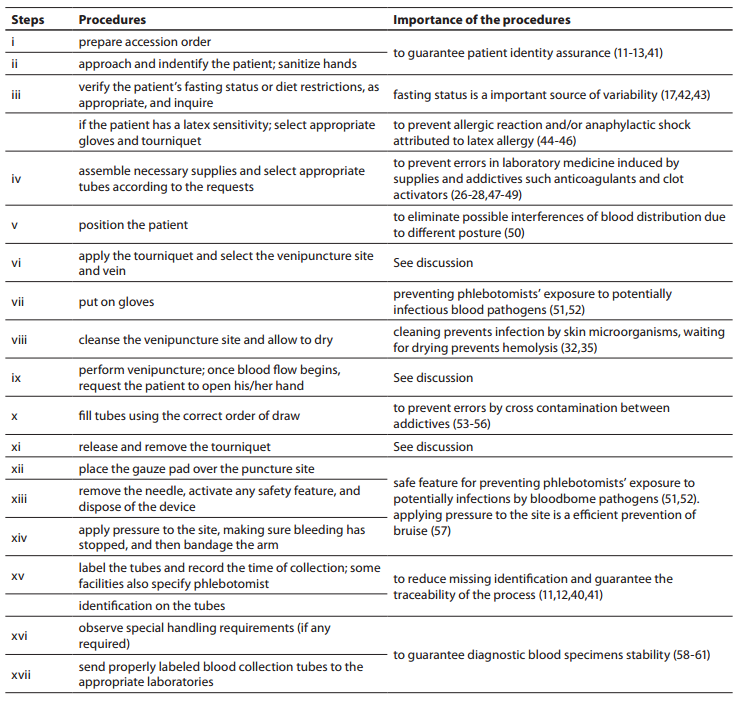
Thirty phlebotomists from São Paulo state, Brazil, previously evaluated (38) were invited to participated in this study. Each phlebotomist was trained individually to perform exactly the venipuncture procedure from CLSI H03-A6 document (36). The phlebotomy training program was realized during 8 hours where the importance of each step of the procedure was explained (Table 1). Only one external/expert auditor from DICQ (39) trained all phlebotomists in one month (from October to November 2011). DICQ is a National System of Accreditation from Brazilian Society of Clinical Analyses. This accreditation system is based on ISO 15189 (40). After the training, all phlebotomists were monitored for twenty working days, to guarantee the assimilation of the correct procedures for the collection of diagnostic blood specimens, in conformity with the CLSI H03-A6 document (Table 1). Only after this period of time the phlebotomists participating in the present study were revaluated. This period of time is considered sufficient by quality laboratory’s managers for incorporating new procedures. Obviously we chose to train and revaluate the same thirty phlebotomists previously assessed by Lima-Oliveira et al. (38), because we were aware of the delicateness of the workday routine of these professionals.
Table1. Procedures for the collection of diagnostic blood specimens by venipuncture from CLSI H03-A6 document (36) used during phlebotomy training program.
Evaluation of the phlebotomist performance
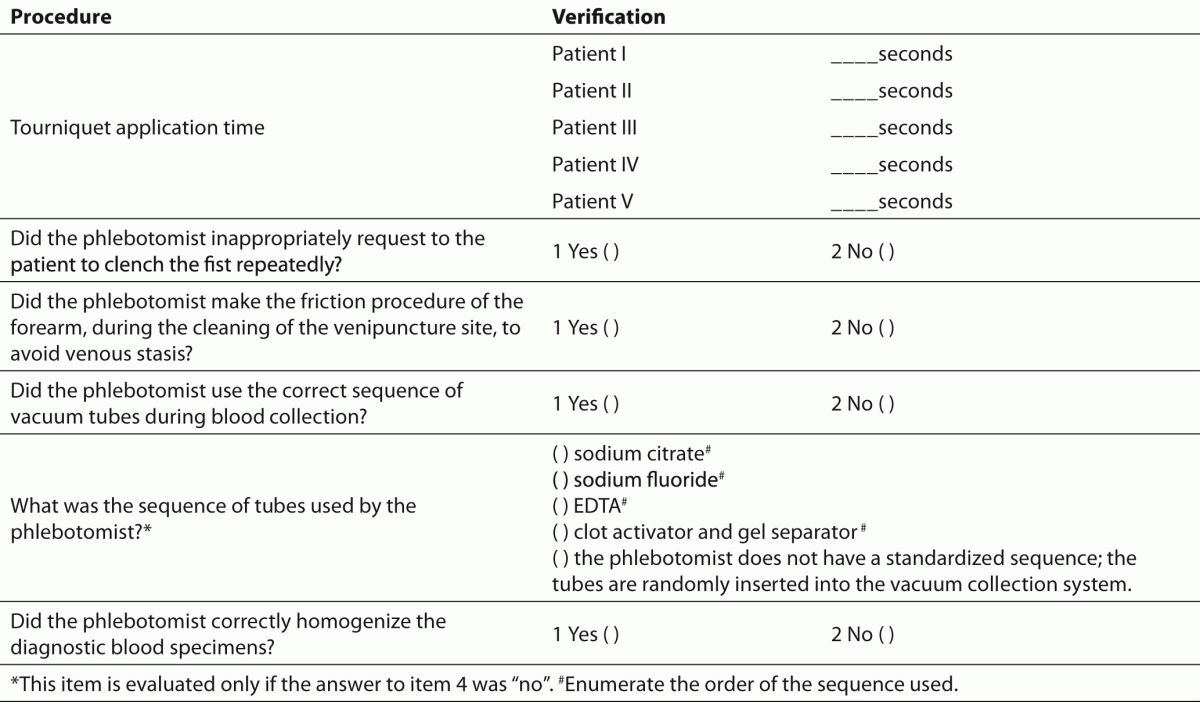
To assess the performance of phlebotomists during the collection of diagnostic blood specimens the check list (Table 2) previously used by Lima-Oliveira et al. was followed (38). This check list allowed the evaluation of whether procedure for blood collection by venipuncture from CLSI H03-A6 document (36) was able to improve the quality process, or if it introduced greater variability and consequently more errors in clinical laboratory testing.
Table 2. Checklist to assess the performance of phlebotomists during collection of diagnostic blood specimens by venipuncture.
Statistical analysis
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to assess the normality of distribution of tourniquet application time. All parameters in our study were normally distributed. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Differences were tested by paired Student t-test. Fisher exact test two-tailed, was used to compare qualitative phlebotomy procedures differences between laboratories before and after phlebotomy training program. McNemar Chi-square test for dependent samples was used to compare before-after laboratories training. The values P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed with Statistica for Windows, version 8.0 (StatSoft Inc.,Tulsa, OK, USA).
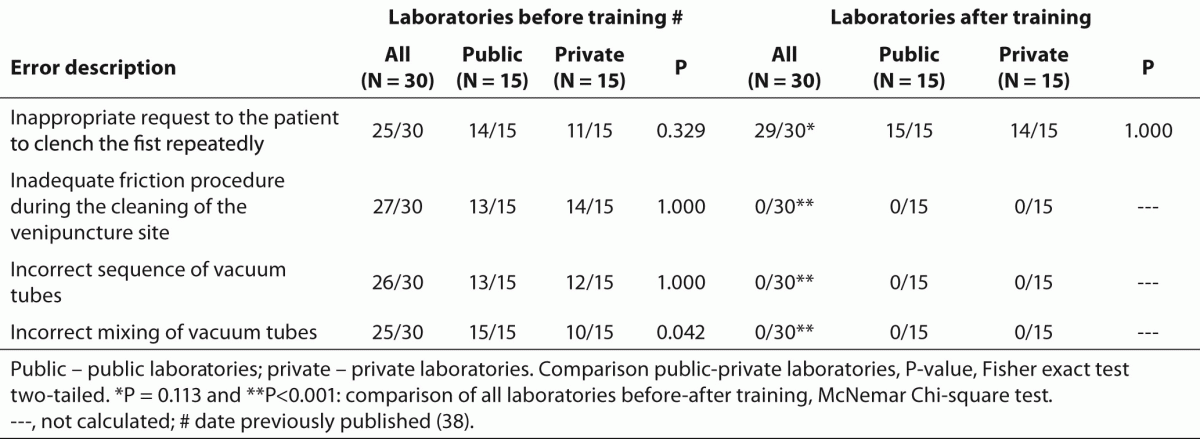
Table 3. Relevant error sources associated to phlebotomy procedure before and after phlebotomy training program.
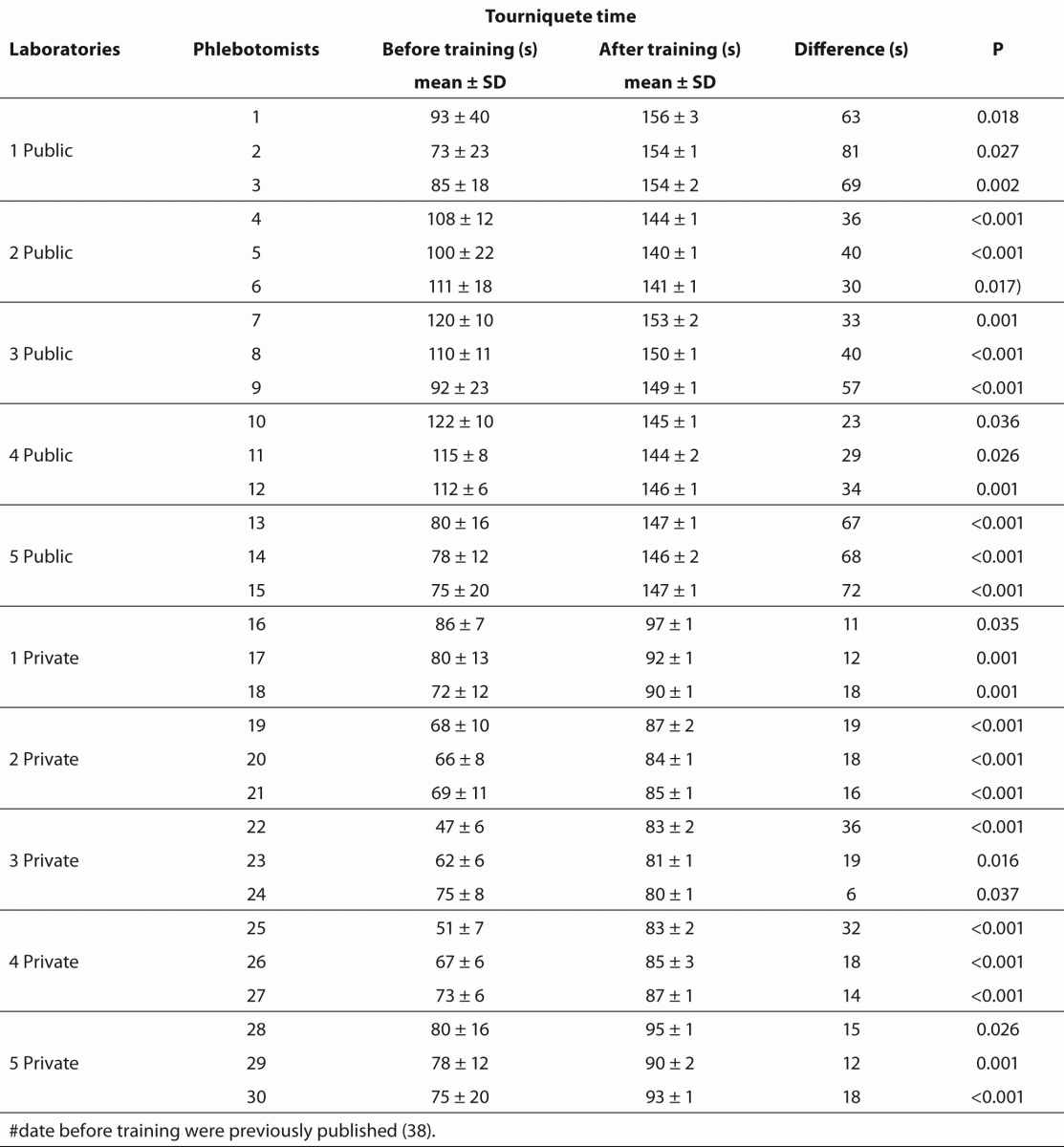
Table 4 Effect of phlebotomy training program on tourniquet application time.
Results
Survey
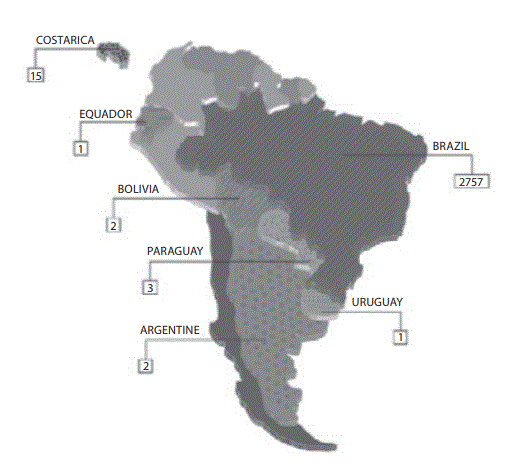
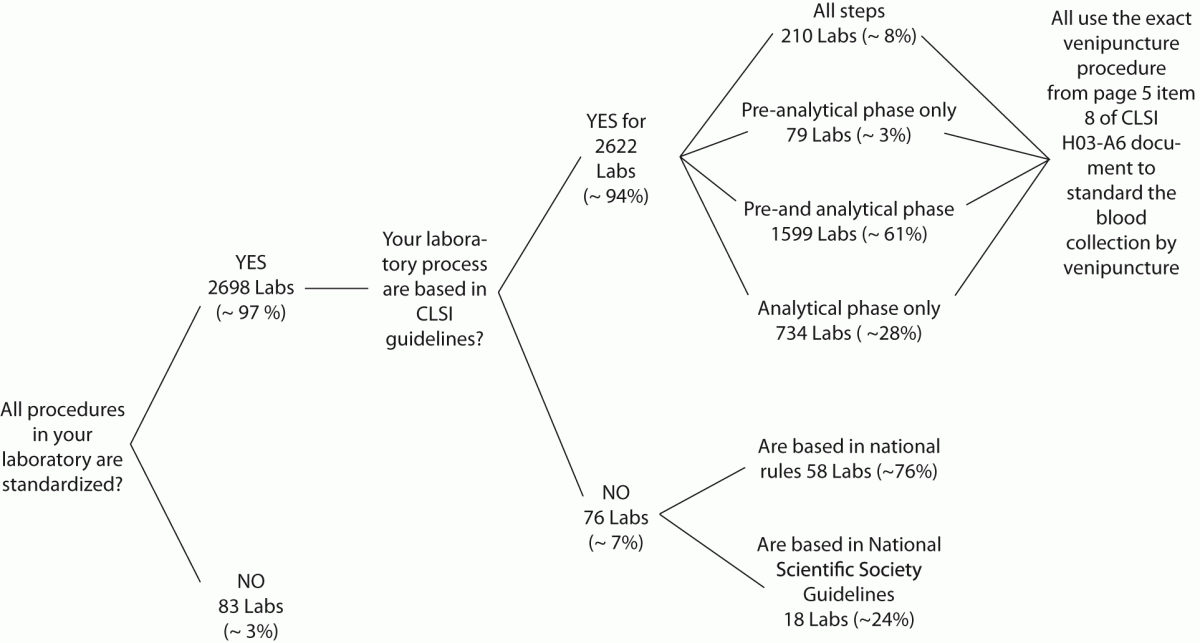
The answers from 2781 laboratories were received throughout the study period (i.e., 60 days), that is ~76% of the total previously predicted (Figure 1A). After this period the collection of data was stopped. The results of the survey are shown in Figure 1B.
Figure 1. Representativeness of CLSI documents in South American
Figure 1A: Geographic distribution of evaluated laboratories by survey.
All evaluated countries are showed textured. The absolute number represents the group of laboratories evaluated by countries.
Figure 1B: Survey results.
Labs: laboratories.
Phlebotomy training program
The training of phlebotomists for 20 days before our evaluation completely eliminated a series of non-conformity, including i) incorrect friction on the forearm during the cleaning of the venipuncture site to produce venous stasis and ease vein location; ii) incorrect sequence of vacuum tubes collection (i.e., incorrect order of draw); and iii) inadequate mixing of blood in primary vacuum tubes containing anticoagulants or clot activators (Table 3). Regarding tourniquet time (Table 4) the overall mean ± SD was 118 ± 1 s. Private laboratories applied the tourniquet for significantly shorter times than public laboratories (87 ± 1 s vs. 148 ± 1 s; P < 0.001). All the phlebotomists inappropriately requested the patient to clench the fist repeatedly (i.e., more than twice).
Discussion
Our survey shows that CLSI documents are widely used in South America as 2622 from 2781 laboratories appear compliant with these documents to standardize their procedures. The CLSI mission is to develop best practices in clinical and laboratory testing, as well as promoting their use worldwide, using a consensus-driven process that balances the viewpoints of industry, government and healthcare professionals (62). Lima-Oliveira et al. previously showed that phlebotomists’ procedures from private- and public laboratories are not harmonized (38). The results of this study shows that the venipuncture procedure training following CLSI H03-A6 document (36) was ideal to harmonize the activities both within-laboratory and between-laboratories (Table 3). This CLSI document standardized important steps; a critical analyze of the importance from each step are show in table 1. As reported, seldom the expert phlebotomist concludes the collection of diagnostic blood specimens within sixty seconds of tourniquet application or even more (38). From a practical point of view, the tourniquet induced venous stasis promotes the exit of water, diffusible ions and low molecular weight substances from the vessel thereby increasing the concentration of various blood analytes at the punctured site thus potentially influencing the laboratory results interpretation (18). More so, when the vascular microenvironment is subjected to both hypoxia and concurrent stasis, accumulation of some bioproducts ensues, such as protons that have the potential to promote changes in laboratory parameters (63). It is noteworthy that the time of tourniquet application was increased significantly (P < 0.05) in all phlebotomist evaluated after training with CLSI H03-A6 document (36). Several concurrent causes might contribute to lengthen the tourniquet time even over 3 minutes, such as a difficult location of an appropriate venous access, the selection of the most suited blood collection system, the insertion of the needle into the vein, the collection of many tubes (18), but here we verified that the procedure from CLSI H03-A6 document(36) per se increased the tourniquet time application. In such case, the caring physicians unaware of the real patient situation might abstain from appropriate treatments as a consequence of venous stasis (18-21,23,24)caused by venipuncture procedure from CLSI H03-A6 document (36). Paradoxically, while the CLSI H03-A6 document (36) advises that the tourniquet application should not exceed one minute, on the other hand the standardization of the various activities according to the document itself entails a tourniquet time of more than one minute. Based on our results, we suggest to put on gloves (step vii), to cleanse the venipuncture site and to allow to dry (step viii) before applying the tourniquet and selecting the venipuncture site and vein (step vi). Moreover we recommend to release and remove the tourniquet (step xi)immediately when the first tube start to fill. These proposals will help to reduce the tourniquet application time and consequently to eliminate important source of errors e.g. venous stasis and hemolysis (18-21,23,24,32,34,35).We have also shown that private laboratories continue to display a significantly lower time of blood collection than public facilities after the training period (i.e., 87.6 ± 1.6 s vs. 147.1 ± 1.9 s; P < 0.001). A reliable explanation for this is that private labs have more ergonomic furnitures in blood collection rooms. Several studies and laboratory quality management documents showed that the clenching of the forearm before venipuncture modifies the concentration of several analytes in blood, especially potassium (this is probably due to hemolysis) (32,64-66). Unfortunately the laboratories staff that collect blood still request “pumping” to aid venipuncture. It has however been reported earlier that this unnecessary activity can be eliminated since a suitable vein access can be reliably identified by using a transilluminator device (18-20,67-69).
In conclusion, the wide distribution and implementation of the CLSI H03-A6 document can improve the laboratory quality process, although the steps for collecting diagnostic blood specimens by venipuncture can still not be considered a gold standard, since they might inherently promote errors. The tourniquet application time and forearm clenching should be verified by all quality laboratory managers in the services. Accordingly, the venipuncture procedure should be revised to eliminate this source of laboratory errors and safeguard the quality throughout the total testing process.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all quality laboratory managers that agreed with this re-evaluation and to their phlebotomists. Our special thanks for Mr. Stefano Ferrante for designing Fig. 1.