Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: Copyright Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Copyright: 2024, Copyright Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/):
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) 4.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 04 December 2023
Date accepted: 13 March 2024
Publication date: 15 June 2024
Publication date: 15 June 2024
Volume: 34
Issue: 2
Electronic Location Identifier: 020502
Publisher ID: bm-34-2-020502
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2024.020502
Hairy cell leukemia – etiopathogenesis, diagnosis and modern therapeutic approach
Katarzyna Maćkowiak[1]
Magdalena Jankowiak[1]
Karolina Szewczyk-Golec[2]
[1] Department of Laboratory Diagnostic, Dr Jan Biziel University Hospital No. 2, Bydgoszcz, Poland
[2] Department of Medical Biology and Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Ludwik Rydygier Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Poland
[3] Department of Pathobiochemistry and Clinical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ludwik Rydygier Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Poland
Author notes:
[*] Corresponding author: igaholynska@cm.umk.pl
Author contributions
K Maćkowiak: conceptualization, writing orginal draft. M Jankowiak: conceptualization, writing orginal draft. K Szewczyk-Golec: writing – review & editing, visualization. I Hołyńska-Iwan: writing – rewiev & editing, formal analysis.
• A chronic lymphoproliferative disease with characteristic mature clonal B lymphocytes with hairy protrusions
• Associated with impaired activity of the B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (BRAF) protein
• Differential diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia, hairy cell leukemia variant and splenic marginal zone lymphoma allows for the selection of effective pharmacological therapy and for risk stratification
• Therapeutic approach includes purine analogues, BRAF kinase inhibitors, and anticancer immunotherapy
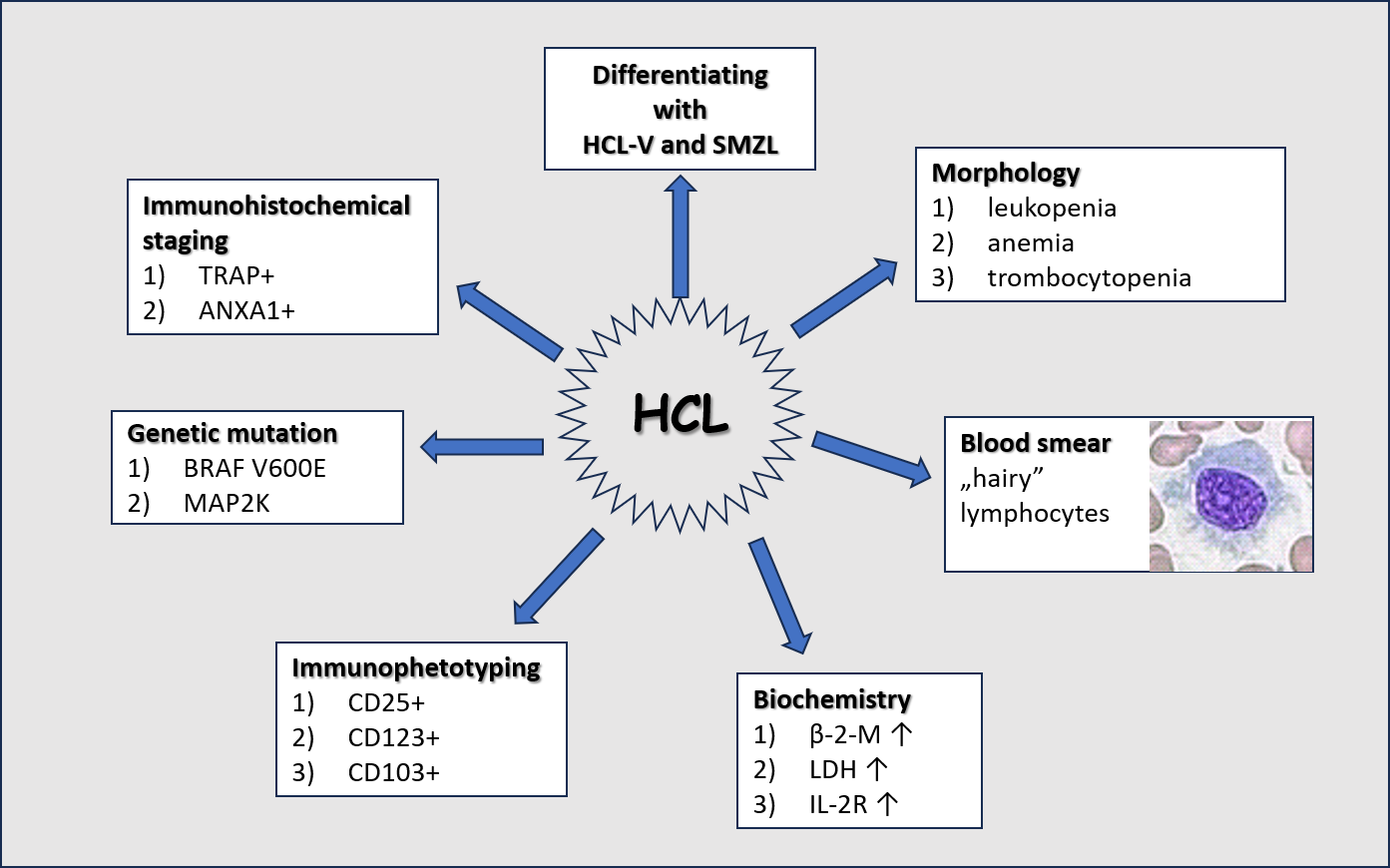
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) represents 2% of all leukemia cases, with men aged above 55 years being the most affected. The most common symptoms of this type of leukemia include splenomegaly, monocytopenia, and neutropenia. In the basic blood count examination, leukopenia with monocytopenia and granulocytopenia, as well as aplastic anemia and/or thrombocytopenia occur. The mutation of β-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (BRAF) proto-oncogene, which can be found in nearly 100% of patients, is an important feature of HCL. Immunophenotypic analysis of the HCL cells reveals high expression of B-lineage antigens, including CD19, CD20, and CD22. Additionally, CD11c, CD25, CD103, and CD123 belong to specific markers of HCL. Lactate dehydrogenase activity and β-2-microglobulin concentration are also important in the patient’s assessment. The differential diagnosis between HCL, hairy cell leukemia variant (HCL-V) and splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is of first importance. Currently, the main treatment for HCL involves the use of purine analogues, excluding pregnant women, individuals with severe infections, and those with relapsing HCL.
Keywords: BRAF V600E; hairy cell leukemia; purine analogues; cancer; molecular hematology