Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: ©Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Copyright: 2023, Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry
License (open-access):
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 09 April 2024
Date accepted: 24 October 2024
Publication date: 15 December 2024
Publication date: 15 February 2025
Volume: 35
Issue: 1
Electronic Location Identifier: 011002
Publisher ID: bm-35-1-011002
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2025.011002
Red blood cell agglutination caused by ceftriaxone and its effect on erythrocyte parameters: a case report
Renata Zrinski Topic[1]
[1] Department of Medical Biochemistry and Hematology, Children’s Hospital Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia
[2] Department of Pulmonology, Allergology, Immunology and Rheumatology, Children’s Hospital Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia
[3] School of Medicine, University of Split, Split, Croatia
[4] University Department of Nursing, Catholic University of Croatia, Zagreb, Croatia
Author notes:
[*] Corresponding author: petra.andrasic@gmail.com
Author contributions
P Andrasic: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - original draft; R Zrinski Topic: Supervision, Validation - Verification, Writing - review & editing; I Pavic: Investigation, Writing - review & editing; J Lenicek Krleza: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation - Verification, Writing - review & editing.
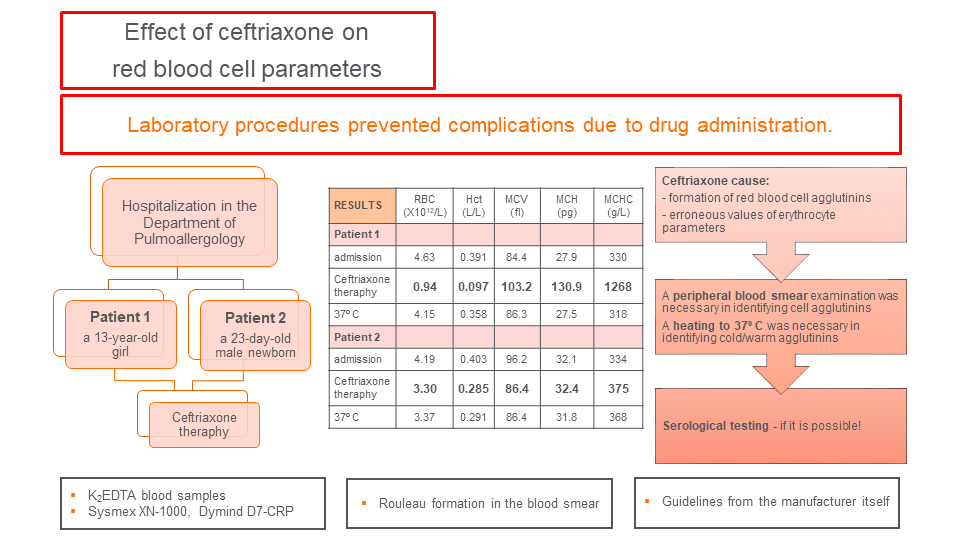
• Ceftriaxone led to the formation of red blood cell agglutinins
• Ceftriaxone causes erroneous values of red blood cell parameters
• A peripheral blood smear was necessary to identify cell agglutinins
• Laboratory procedures prevented complications due to drug administration
• Cessation of ceftriaxone is crucial in preventing life-threatening complications
Ceftriaxone, a widely used antibiotic, is one of the most common drugs to cause drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia. In this report, we describe the effect of ceftriaxone on red blood cell parameters (low red blood cell count, low hematocrit, and high erythrocyte index values) in two pediatric patients without clinical symptoms of hemolytic anemia. Although automated hematology analyzers have helped to detect incorrect results, a peripheral blood smear examination was necessary for recognizing the erythrocyte agglutinins caused by ceftriaxone. Serological testing was not possible, but the resulting drug-induced antibodies mimicked cold agglutinins in the first patient and warm agglutinins in the second patient. Timely reactions and corresponding laboratory procedures prevented potential complications due to drug administration. This report aims to present laboratory findings and preanalytical challenges in these cases and share our experiences in solving them.
Keywords: agglutination; ceftriaxone; hemolytic anemia; preanalytical errors; red blood cell count